INFN
INFN
INFN is a public research agency under the supervision of the Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR). It conducts theoretical and experimental research in fundamental physics, within a framework of international competition, in collaboration with universities. This requires the use of cutting-edge technology and instruments, developed by INFN at its own laboratories and in collaboration with industry.
Today INFN employs some 5,000 scientists whose work is recognised internationally.
Science and technology at INFN
The lines of research conducted at INFN are subnuclear physics, astroparticle physics, nuclear physics, theoretical physics, technological and inter-disciplinary research.
INFN carries out research activities at two complementary types of facilities: divisions and national laboratories. The four national laboratories, based in Catania (LNS), Frascati (Rome) (LNF), Legnaro (Padua) (LNL) and Gran Sasso (L’Aquila) (LNGS), house large equipment and infrastructures available for use by the national and international scientific community. Each of the 20 divisions are hosted by university physics departments and guarantees close collaboration between the INFN and the academic world. Further, three national centres, devoted to technological and educational activities are part of the INFN facilities: the National Centre for Research and Development in Information Technology (CNAF), based in Bologna, the GSSI, Gran Sasso Science Institute, in L'Aquila, and the Trento Institute for Fundamental Physics and Applications (TIFPA).
INFN’s contribution to ESS
In BrightnESS, INFN is involved in Work Package 2: Strengthening In-Kind Contribution and Coordination. The objectives for this Work Package is to maximise the possibility for ESS and In-kind partner organisations to deliver value during the Construction Phase through In-Kind Contributions according to the ESS IKC Process. INFN is also involved in Work Package 6: Collaboration, Communication and Dissemination.
INFN contributes to the construction and operation of ESS with resources made available by the Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR). The following three Italian public research institutions are involved: INFN, holding the role of representing entity for Italy, the National Research Council (CNR) and Elettra Synchrotron Trieste. ESS is of strategic value for Italy: on one hand, it provides a unique opportunity for basic and applied scientific research, on the other hand, a strong R&D effort will involve high-tech industries.
INFN contributes to the construction of the ESS accelerator with the following unit and National Labs:
- LNS: management of the Warm Section of the LINAC, proton source and beam shaping region (LEBT);
- LNL and Unit of Turin: Drift Tube Linac, i.e. the part of the accelerator up to 90 MeV
- Unit of Milano-LASA: medium beta superconducting elliptical cavities.
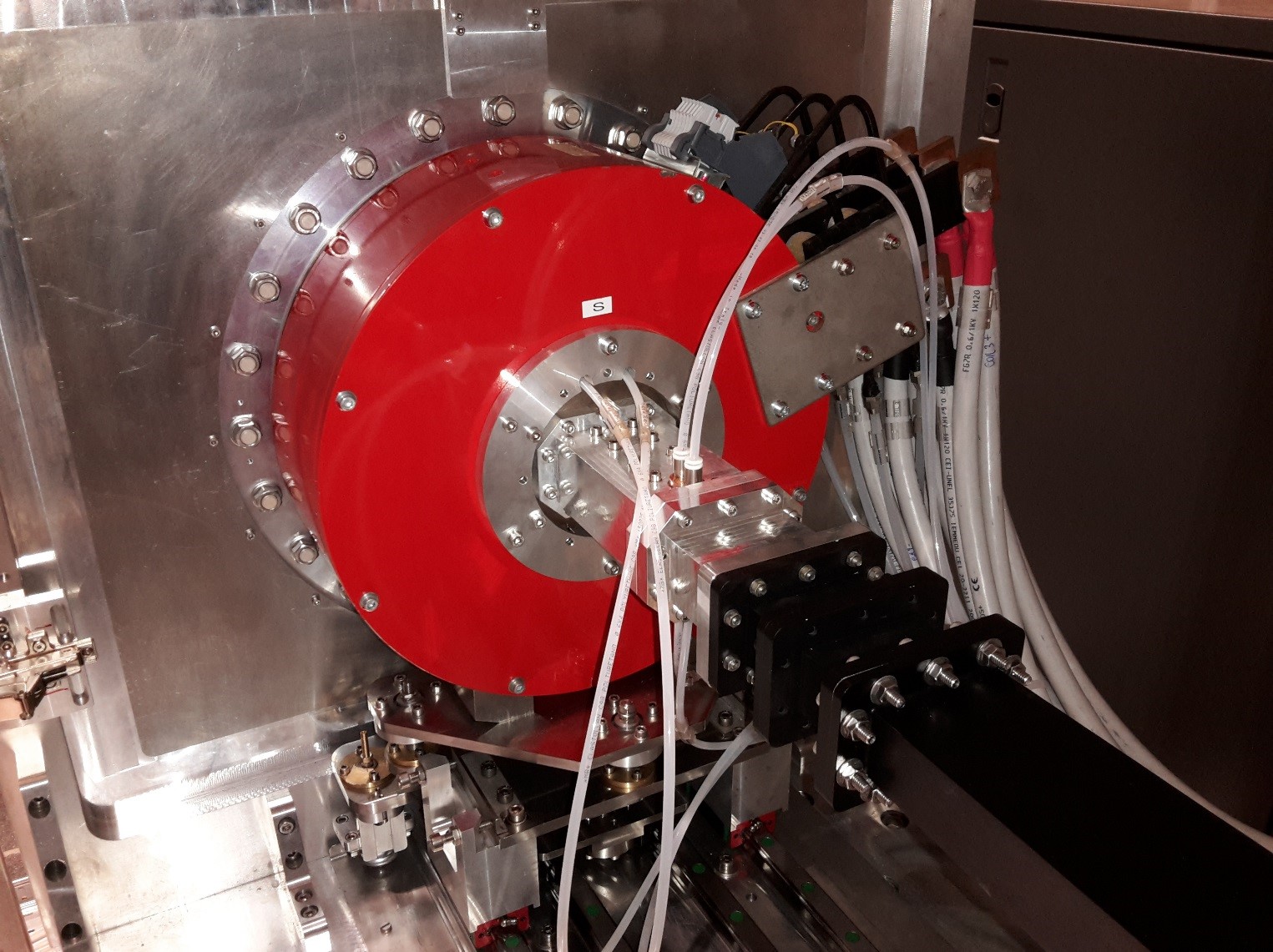
A proton source built at the Southern National laboratories of INFN.


 is funded by the European Union Framework Programme for Research and Innovation Horizon 2020, under grant agreement 676548.
is funded by the European Union Framework Programme for Research and Innovation Horizon 2020, under grant agreement 676548.